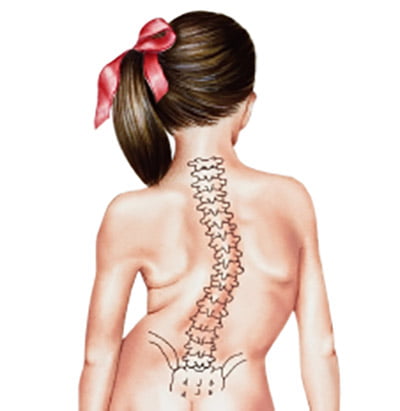
Scoliosis, developing in early adolescence, is a condition in which the patient suffers from an abnormal curve in spine in the shape S or C. The disease is a bit difficult to detect, because in early stages it doesn’t cause any pain and appears gradually.
Structural changes common with Scoliosis–
The structure of human spine appears straight in normal conditions. The building blocks that make up the spine are called the vertebrae and are responsible for the usual posture of the body. The people affected by Scoliosis suffer from a curve in spine that’s makes them appear tilted on one side.
S-shaped curves, called “double curves” are more likely to deteriorate over time and the solid skeletal framework gets fragile or tilted further. C-shaped curves have lesser tendency to worsen.
One eventually gets to know about having scoliosis, because the curvature of spine gradually becomes more prominent. The doctor physically examines the spine, ribs, hips, and shoulders. With the aid of a tool called an inclinometer, or scoliometer, the doctor can measure the degree of curvature of spine (scoliosis).
However, people around a newborn can also stay vigilant about the developments of the new born. Since it is a disease that is found in millions every year as per reports, a watchful eye will always help detect the case early.

Symptoms to watch out for –
- One shoulder blade that appears more prominent than the other.
- One hip higher than the other
- A rotating spine or movement of spine beyond normal
- Problem in breathing because of reduced area in the chest for lungs to expand
- Back pain
How can early diagnosis of Scoliosis make things better?
- Surgery can be completely avoided.
- The condition of the patient can be improved considerably if diagnosed with mild or moderate scoliosis – Over time with synchronized teamwork between the patient, healthcare givers and the family the condition can be improved with various therapies like Schroth therapy, Casting or Bracing etc
- Also, the fight with scoliosis is an ongoing process, so, early the start, better the results.
Which category of Scoliosis the patient’s case might be similar to??
Common Types –
- Idiopathic scoliosis, the most common in which the cause of the disease is not known. It is categorized by the age groups
- Infantile idiopathic scoliosis -If the patient is less than 3 years old
- Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis- The one that develops between 3-10 years of age
- Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis – In patients who are over 10 years old (10-18 years old)
- Kyphoscoliosis: a combination of outward and lateral spine curvature
- Dextroscoliosis: curvature of the spine to the right
- Rotoscoliosis (rotatory): curvature of the vertebral column turned on its axis
- Levoconvex: curvature of the spine to the left
- Thoracolumbar: curvature related to both the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spine

Available treatment procedures – Non Surgical-
- Observation: A large number of patients (mostly children) don’t need treatment because of the presence of a very mild curve, but they are kept on observation for 4 to 6 months to see if treatment is needed.
- Casting: In case of infants a cast made of plaster of paris is used, which is worn by the child. This helps in reducing the spine curvature. The cast is changed regularly because of the growing child.
- Bracing: Similar to casting braces are also used to prevent further curve in spine. It is worn all the time by the patient.
- Schroth therapy- This therapy is a three dimensional approach that addresses the curve in spine in three dimensions front to back, left to right and transverse. It is combination of routine exercises that have proven results of improving the condition.
- Magnetic approach- It’s a non invasive painless treatment method for scoliosis and is proved effective in elimination of the requirement of repeated expansion operations.
Probable Causes —
In most of the cases the cause of the disease is not identifiable, but it is often diagnosed during the first seven years of a child’s life.
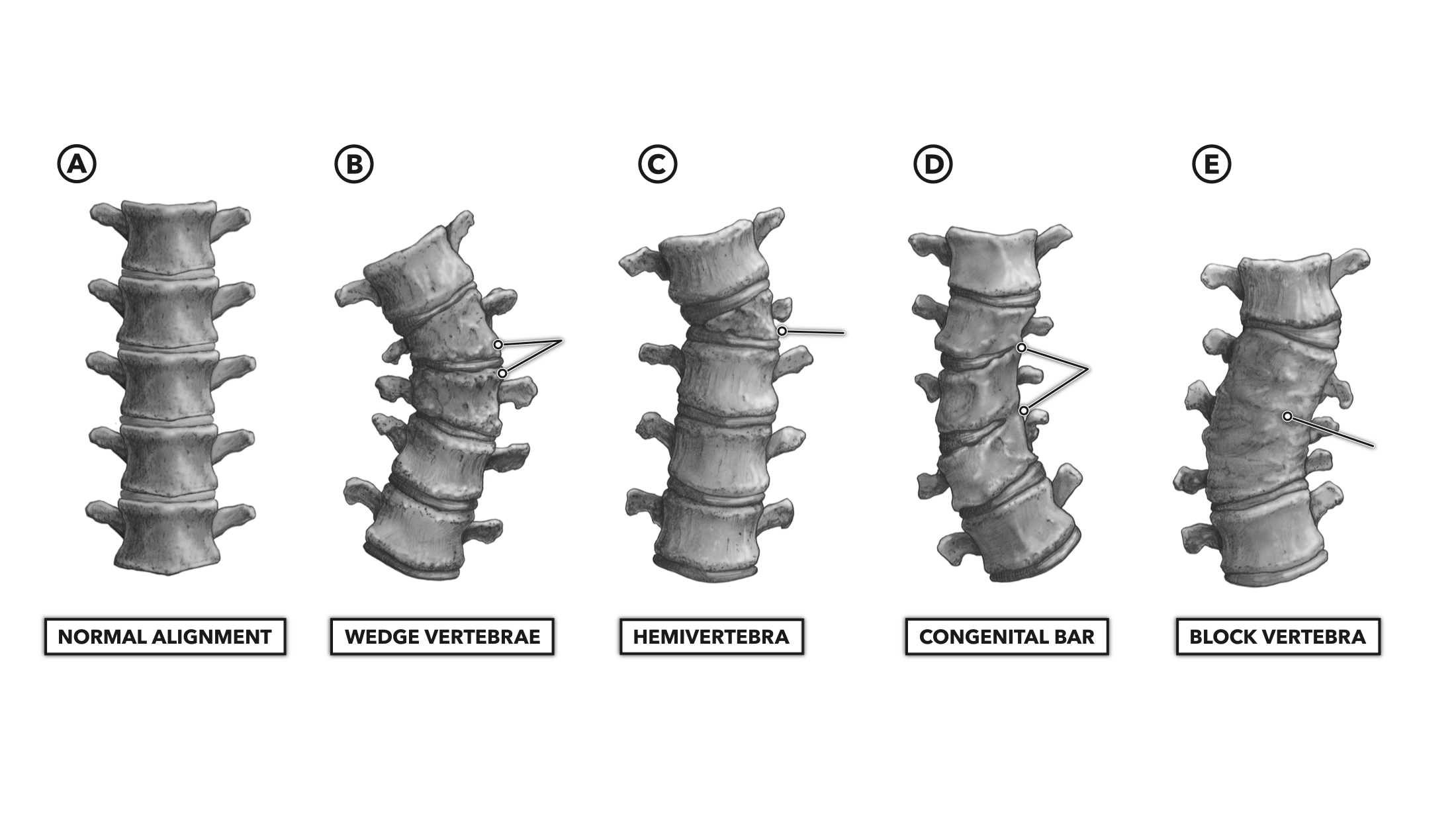
- Congenital scoliosis (present at birth) – This is rare and occurs during pregnancy when bones in the spine develops abnormally in the fetus growing inside the mother.
- Genetic mutations: Various genetic mutations are responsible for improper development of body. Researches and genetic mapping are being done to understand the triggers behind this disease.
- Leg length: If one leg is longer than the other, the individual may develop scoliosis.
- Syndromic scoliosis: Scoliosis can originate as part of another disease aftermaths, including Marfan’s syndrome & neurofibromatosis
- Neuromuscular conditions: These affect the nerves & muscles and include cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy and poliomyelitis.
- Osteoporosis: This can cause secondary scoliosis due to bone degeneration.
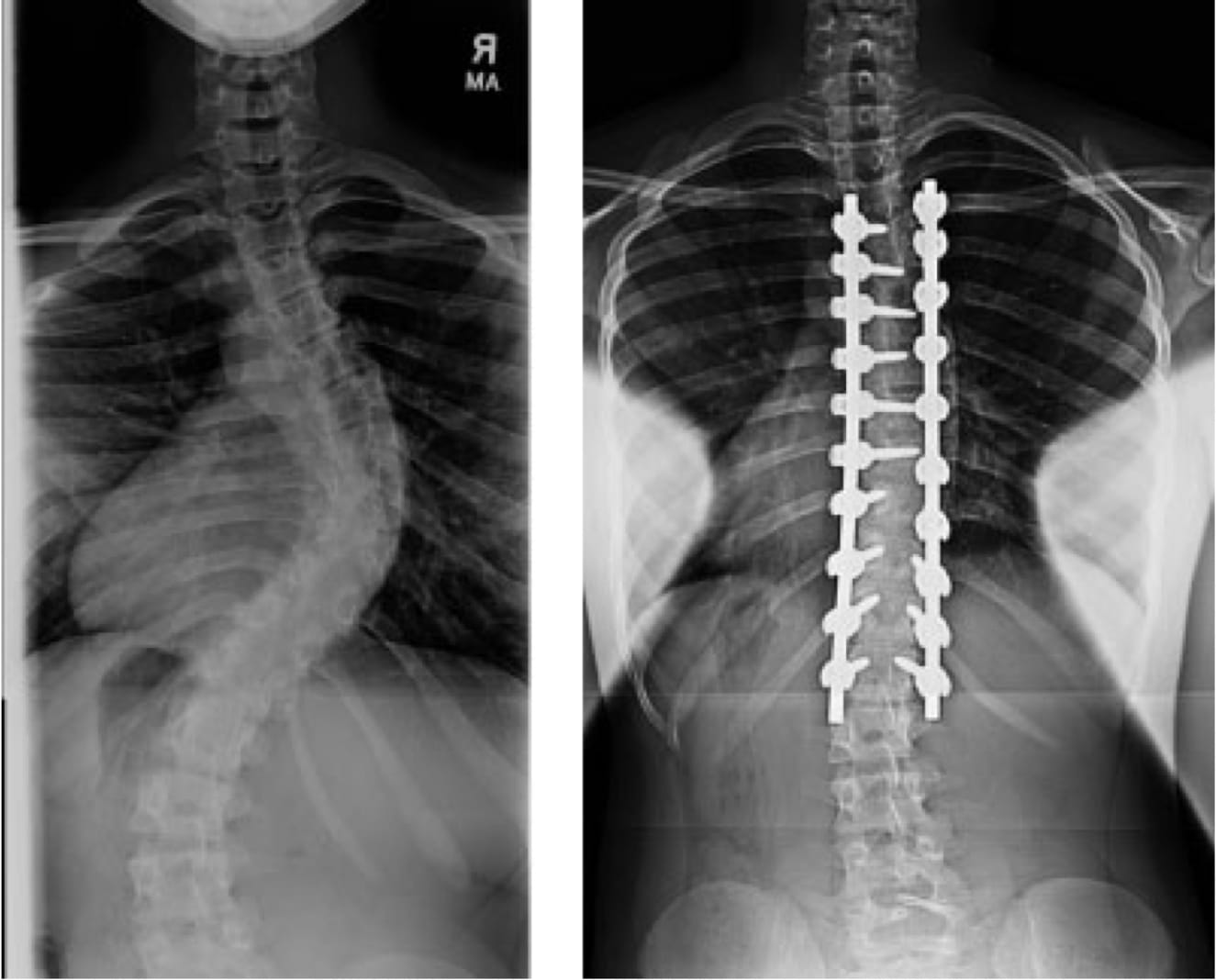
Scoliosis is serious and if identified at advanced stages, the only treatment available is to undergo surgery. Surgeons try correcting the spinal curvature (by spinal fusion) through screws, hooks, rods to keep it straight. They place a bone graft which grows and becomes solid later on to provide a straight shape to the spine.
However, the risk of complicated surgeries like any other surgery remains. So to prevent & reduce risks/ side effects, surgeons often use neuro -monitoring during surgery.