Fibrous dysplasia is cancer of bones that result in the formation of abnormal fibrous tissue in place of normal bone. This is a non-cancerous condition of bones that leads to several problems within bones.
Cancer weakens the bones after the fibrous tissue grows and expands with time. This leads to deformation or fracture of bones. Some patients who suffer from this condition experience no or few symptoms.
However, in other cases, it affects multiple bones, and the situation becomes more severe. Thus, many patients require surgery that removes the diseased part of the bone. This helps repair or prevent bone fractures and other deformities.
Fibrous dysplasia occurs when mutations in the genes occur. Although it is a genetic disorder, the parents do not cancer to their children. No cure is there, and the treatment usually includes surgery, which helps relieve the pain and stabilize bones.

What leads to the condition?
The disorder occurs when the cells that produce bone develop certain mutations in genes. Due to these mutations, the production of irregular and immature bone tissue occurs.
Most of the time, this lesion (irregular bone tissue) occupies a single site on a bone. However, there are cases when it affects multiple bones. Also, more than one lesion may occur on multiple bones.
At puberty, these lesions usually stop growing. However, during pregnancy, the lesions may develop again. The mutation responsible for the disorder usually occurs in the early stages of fetal development that is after conception. This is why one cannot inherit this mutation to their offspring or get one from their parents.
Symptoms.
In certain cases, painless lesions may develop and no symptoms are there. Thus, the diagnosis of cancer mostly occurs accidentally. You often detect it while performing an x-ray for some other health issue or medical condition.
While when symptoms are there, it shows that the lesion is larger and more severe now. Below are some signs and symptoms that you should be looking for:
Pain. The growth and expansion of fibrous bone tissue result in the weakening of bones. This results in pain, which may be severe in case cancer affects the weight-bearing bones of the body like legs or pelvis.
The pain may progressively worse over time, which usually begins as a dull ache initially. Furthermore, the pain increases with the activity and decreases when you rest.
Fracture: The disorder weakens the bones. Thus, the bones are much weaker at the place of the lesion. This results in a fracture of the bone, which causes sudden and severe pain. Although the fracture may occur suddenly with no pain at all, however, a period of dull pain may be initially present.
Deformation of bones: Regular and repeated fractures may cause poor healing. Thus, bone deformities are some common signs under these circumstances. The deformity can become highly noticeable if present in the face or bones of the legs.
Thus, loss of vision or hearing may also occur. One may also develop arthritis or have trouble walking if the pain is present in the legs or pelvis.
Hormonal disturbances: Several hormonal abnormalities may also occur. Thus, early puberty in young patients is the consequence of the disorder. Furthermore, girls develop a problem more often than boys.
This occurs because of the hyperactivity of the ovaries. However, it may occur in other glands as well, like the thyroid, pituitary, adrenal and parathyroid gland.
Discoloration in the skin: Fibrous dysplasia and hormonal disturbances often lead to other symptoms like discoloration. Therefore, patients with this condition may develop pigmentation in the skin.
How your doctor will examine the disease:
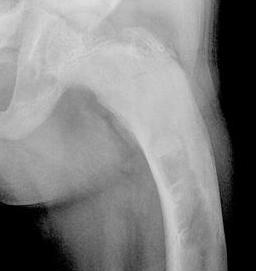
An X-ray is a basic and primary method that your doctor will use for the detection of fibrous dysplasia. In an X-ray, a bone appears solid, while a different appearance is present in the bones with fibrous dysplasia. These distinct appearances are called “ground glass.” Therefore, an X-ray is a good way to diagnose cancer, even in patients with no symptoms.
One may be taking this X-ray for some other ailment. Furthermore, the extent of damage and the presence of deformities will become clear when your doctor orders you an X-ray. In addition to an X-ray, your doctor may perform some additional tests to confirm the condition. These tests include:
Imaging tests. Your doctor may use an MRI or a CT scan to confirm cancer. These techniques help produce 3-D images as well as a cross-section of a bone. The quality of the bone damage or other fractures is going to become clear when you perform these tests.
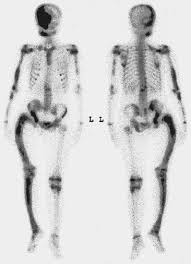
Bone scan. In this nuclear imaging test, your doctor is going to inject a little amount of radioactive tracer into your blood. The damaged portions of the bone will take this dye.
Then, a technician will use a special camera to scan and take the images of your bone. Thus, these images aid your doctor in identifying the lesions in bone.

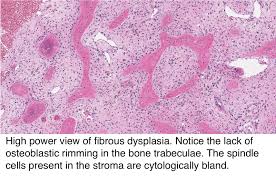
Biopsy. In this invasive technique, your surgeon will remove a small part of the bone using a hollow needle. Then, this your doctor will perform microscopic analysis on this part and confirm the test. The arrangement and structure of cells will help your doctor confirm cancer.

Treatment
There is a low chance of developing a deformity or a fracture if your fibrous dysplasia is mild. Many of the times, one discovers the lesions incidentally. Therefore, your doctor will use an X-ray periodically to monitor your condition.
Medications
Your doctor may use certain medications to control your cancer. For instance, bisphosphonates are some osteoporosis medications the lower the activity of bone dissolving cells (Osteoclasts), thereby preventing bone loss.
Few studies support the idea that these medications strengthen the affected bones and relieve bone pain.
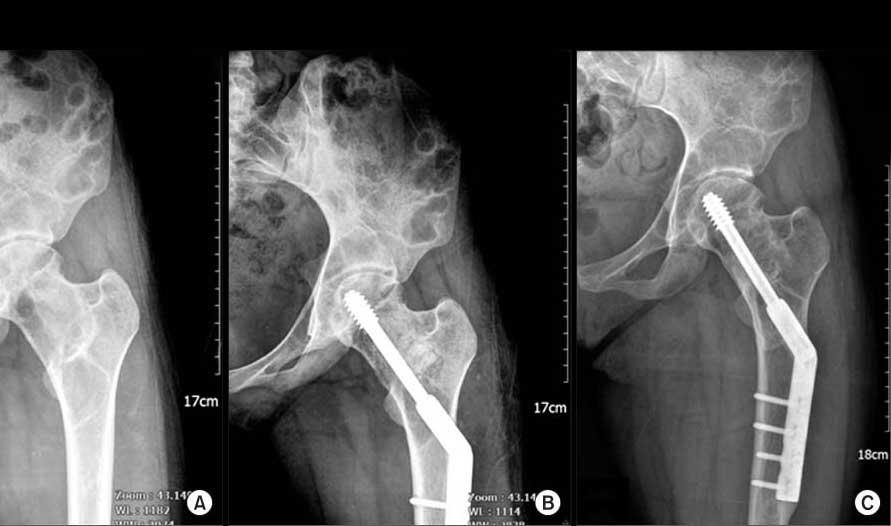
Surgery. In certain circumstances, your doctor may is going to recommend Surgery helps correct a deformity, and repair a fracture that does not get well with casting. Further, it helps in the correction of limb length differences and prevents fractures.
Surgery is helpful if the lesion is present in your skull or face as it helps relieve pressure on nerves. Furthermore, our doctor may also remove your bone lesion and replace the space with a bone graft. This bone graft may be from your own body or a donor.
Nowadays, your surgeon may even use synthetic bone grafts. However, the lesion may develop again in some patients. Your doctor may also stabilize your bone or prevent a fracture by inserting metal plates, screws, or rods.

Coping and support
When you get diagnosed with fibrous dysplasia, it could be frightening for you. The condition will be no different for your family.
However, you may learn to cope with the uncertainty and distress related to cancer with time. Thus, you need to follow these instructions until then;
Call on for medical support:
Various things are going to help you. For instance, the knowledge and understanding of a medical social worker, or any other mental health professional is necessary. They will help you in understanding your cancer.
Furthermore, if your child or other family member suffers from cancer, you need to ask health care professionals for advice. They will provide you with options for medical health support. This will also provide you with emotional and social support.
In addition to this, you can check various online services that will provide you support to combat cancer.
- Gain more knowledge about fibrous dysplasia to make decisions about control and care:
Ask your doctor about various treatment options related to fibrous dysplasia. Little knowledge is dangerous. Therefore, more confidence in understanding and making decisions about treatment options will be there with you. So you should always learn more about the disease.
Ask the health care team for guidance if your child has cancer. Therefore, get more and more information for appropriately caring for the patient.
Be close to your friends and family:
A close and strong relationship with your family and friends is necessary. It will help you deal with fibrous dysplasia.
You need practical support, moral support from your friends and relatives. Thus, someone should be there for you to look after the family. Emotional support from them is going to matter most. Thus, a healthy and happy person will ultimately efficiently fight the disease.
Prepare for your appointment
You are likely to start making an appointment with your primary care doctor if some signs and symptoms worry you. Ask for a referral to an experienced specialist if your doctor suspects fibrous dysplasia.
A team of specialists typically can treat fibrous dysplasia. For instance;
Orthopedic surgeons or orthopedic oncologists who have specialization in operating bone cancers.
Doctors who have a specialization in treating cancers with systemic medications or chemotherapy.
Pathologists diagnose the specific type of cancer by analyzing a tissue.
Rehabilitation specialists who after surgery help in the recovery of a tumor.
What you should expect from your doctor:
You will face several questions from your doctor. Thus, you should be ready to answer these. So, give more time to your doctor to address them. Your doctor may ask;
What signs and symptoms concern you more?
Have your symptoms been occasional or continuous?
When did you start to notice the symptoms?
The severity of your symptoms?
Is there anything that improves your symptoms?
Is there anything that worsens your symptoms?
Do you have any family or personal history of cancer?
