Radiation therapy.
Radiotherapy or Radiation therapy is used as cancer treatment usually abbreviated as RT or XRT in which high doses of radiation are used to kill cancer, shrink tumors less commonly a treatment for blood disorders, thyroid diseases, and no cancerous growths.
Radiotherapy can be curative in few types of cancers if they are restricted to one area of the body. Radiation therapy helps to reduce the size of a tumor before surgery or kill remaining cancerous cells subsequently.
Radiation therapy makes use of energy waves such as heat or light. In radiation therapy, specific machines that produces beam of radiations to target a specific area are used. One more type includes putting radioactive substance inside the body, either temporarily or permanently. Ionizing radiation (high-energy type radiation) is used in cancer therapy. At high doses, radiotherapy kills cancer cells or retard their growth by breaking down the DNA of cancer cells.
Types of Radiation therapy:
The type of radiation therapy depends on many factors, including:
1. Type of cancer
2. Size of the tumor
3. Tumor’s location in the body
4. Location of the tumor and normal tissues that are sensitive to radiation
5. General health and medical history
6. Other types of cancer treatment
7. Age and other medical conditions
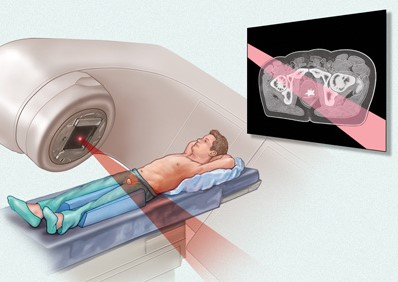
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy is most commonly used. It involves a machine that aims radiation at cancer emitting a beam of radiation. The machine may be noisy and is large. It does not touch the body but moves around, sending radiation to a part of the body from many directions.
External beam radiation therapy is a local treatment, targets cancer that lies deeper within the body.

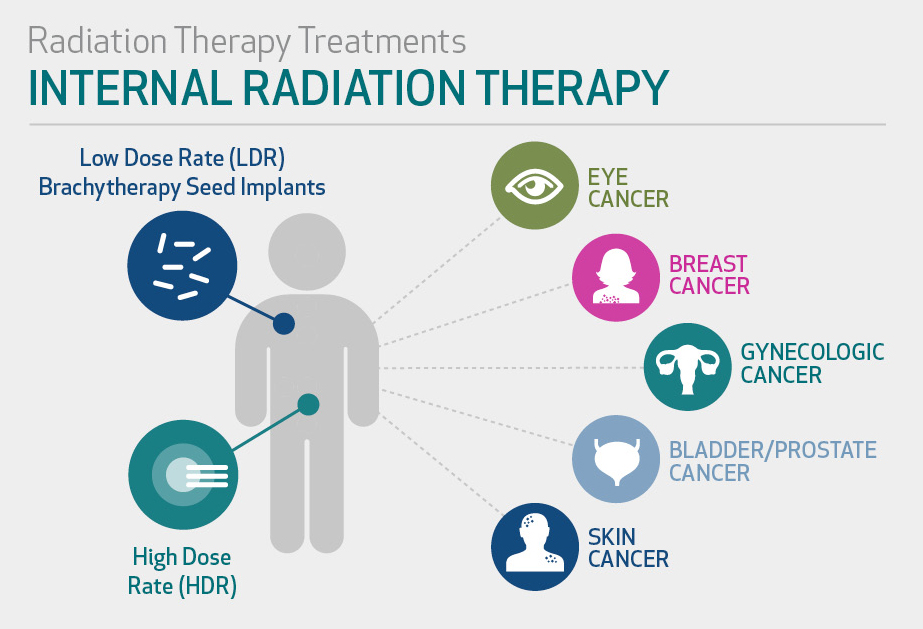
In Internal radiation therapy, y a source of radiation is put inside the body, the radiation source may be solid or liquid.
Internal radiotherapy with a solid source is called. In brachytherapy, capsules, ribbons, or seeds that contain a radiation source are placed in the body, implanted in or near the tumor. The implant can be permanent or temporary. Brachytherapy is a common treatment and targets specific parts.

One more type includes drinking or swallowing or injecting a radioactive liquid via vein with an IV line and is referred to as systemic radiation therapy.
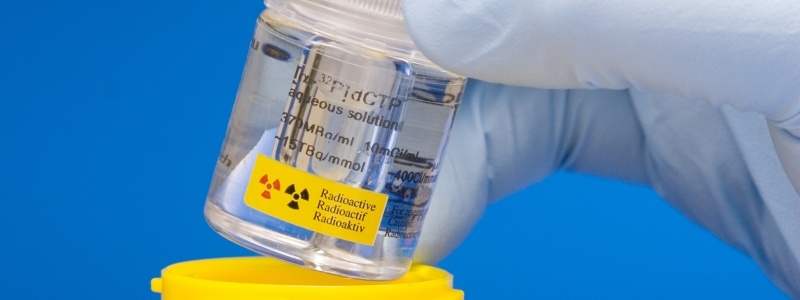

After the systemic radiation therapy, body fluids such as sweat, saliva, and urine may give off radiation for a while.
After receiving radiation therapy, a person may experience:
Emotional distress
Tired ness
Sensitivity near the treatment site
Side effects:
Specific side effects depend upon few factors such as
Area receiving treatment
Person’s overall health
Type and doses of radiation
The side affects associated with the radiation therapy may be both short term or long term.
Short term side effects
Short term side effects of radiation therapy depend upon the body part receiving radiation therapy:
Nausea
Fatigue
Skin changes
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Hair loss may be temporarily permanent.
Long term side effects
Long term side depends upon the treatment site.
They include:
1. lung or heart problems.
2. thyroid problems if radiation affects the chest,
3. May cause hormonal changes (early menopause) if radiation affects a pelvic area,
4. Lymphedema if radiation affects the neck area causes building up of lymph fluid and causes pain.
5. High doses of radiation may increase the chances of forming another cancer. Long-term side effects are not seen in everyone receiving radiation therapy, it depends upon doses given, treatment area, and few other individual factors.
Uses of radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy, in combination with other appropriate therapies, causes cancer to go into revocation. In most cases, it does not come back again.
Radiation therapy may also help to treat symptoms when cancer has spread extensively. At this very moment, radiation is considered as part of palliative care, which aims to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Palliative radiation treatment often involves lower doses and fewer treatment sessions apart from curative treatment.
Palliative radiation treatment may help to stop painful tumors from developing.
Palliative radiation treatment can help in relieving blockage or pressure by reducing tumor size by treating symptoms of brain cancer, such as nausea, dizziness, and headaches
In reducing symptoms of lung cancer, such as breathlessness and chest pain.
In controlling ulcerating, infections, and bleeding.
How much radiotherapy cost?
Radiotherapy can be expensive as it uses complex machines and implicates the assistance of many health care providers. The precise cost of radiation therapy depends on the cost of health care and what type of radiation therapy one gets, and how many treatments one needs.
